gold and silver comparison
Related Articles: gold and silver comparison
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to gold and silver comparison. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Gold vs. Silver: A Comprehensive Comparison of Precious Metals
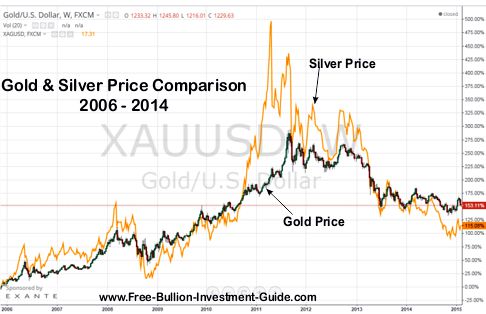
Gold and silver, two precious metals that have captivated humanity for centuries, have long held positions of importance in various aspects of life. From ancient civilizations to modern economies, these metals have served as currency, ornaments, and even industrial components. While both share similarities in their lustrous appeal and inherent value, their distinct characteristics and market dynamics differentiate them significantly. This comprehensive analysis delves into the multifaceted comparison of gold and silver, exploring their historical significance, economic implications, and investment potential.
Historical Significance:
Gold and silver have played pivotal roles in shaping human history. Their discovery and subsequent use revolutionized trade, fostered economic growth, and fueled empires.
- Gold: The allure of gold has been documented since ancient times. Its durability, scarcity, and resistance to corrosion made it an ideal medium for currency and adornment. The Gold Standard, a system where currencies were pegged to gold, dominated the global financial landscape for centuries, providing stability and predictability to international trade.
- Silver: Silver, while less abundant than gold, has also been prized for its beauty and utility. Its use as currency dates back to ancient Mesopotamia, and its role in coinage and trade expanded significantly during the Roman Empire. Silver’s malleability and conductivity also led to its widespread application in jewelry, silverware, and industrial processes.
Economic Considerations:
The economic significance of gold and silver extends beyond their historical roles. In the modern world, they continue to influence global markets and investment strategies.
- Gold: Gold is widely considered a safe haven asset, meaning its value tends to rise during times of economic uncertainty. Investors often turn to gold as a hedge against inflation, currency devaluation, and geopolitical instability. Its limited supply and global demand contribute to its price stability and intrinsic value.
- Silver: Silver’s economic role is more multifaceted. It is both a precious metal and an industrial commodity. Its industrial applications are diverse, ranging from electronics and solar panels to medical devices and photography. As a result, its price is influenced by factors such as industrial demand, economic growth, and technological advancements.
Investment Potential:
Gold and silver have long been favored investment assets, offering potential for capital appreciation and portfolio diversification. However, their investment characteristics and risks differ significantly.
- Gold: Gold’s reputation as a safe haven asset makes it an attractive investment during periods of market volatility. Its long-term price appreciation has historically outpaced inflation, making it a potential hedge against economic downturns. However, gold’s lack of dividend payments and its sensitivity to interest rate changes are factors to consider.
- Silver: Silver’s dual nature as both a precious metal and an industrial commodity makes its investment potential more complex. Its price can be influenced by both industrial demand and investor sentiment. While silver has historically demonstrated higher price volatility than gold, it offers the potential for higher returns during periods of economic expansion and technological innovation.
Gold vs. Silver: A Comparative Analysis:
To understand the nuances of gold and silver investment, it is crucial to compare their key characteristics:
| Feature | Gold | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Rarity | More scarce | Less scarce |
| Price Volatility | Relatively stable | More volatile |
| Industrial Uses | Limited | Extensive |
| Safe Haven Asset | Yes | To a lesser extent |
| Investment Potential | Long-term growth and inflation hedge | Potential for higher returns but greater risk |
| Liquidity | Highly liquid | Generally liquid |
| Storage and Security | Requires secure storage | Requires secure storage |
| Historical Performance | Generally positive long-term returns | More volatile but potentially higher returns |
Factors Influencing Prices:
The prices of gold and silver are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Global Economic Conditions: Economic growth, inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical instability can significantly impact the demand for both metals.
- Investment Demand: Investor sentiment and market speculation play a significant role in driving prices, especially during times of uncertainty.
- Industrial Demand: Silver’s industrial applications influence its price, making it susceptible to changes in technological advancements and manufacturing activity.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: The availability of gold and silver, as well as global demand from various sectors, directly impacts their prices.
- Government Policies: Monetary policies, trade agreements, and regulations can influence the supply and demand of precious metals.
Benefits of Gold and Silver Investment:
While both gold and silver offer potential investment benefits, their specific advantages differ:
-
Gold:
- Inflation Hedge: Gold’s value tends to rise during inflationary periods, preserving purchasing power.
- Safe Haven Asset: Gold provides a safe haven during times of economic uncertainty and geopolitical instability.
- Portfolio Diversification: Gold’s low correlation with other asset classes can help diversify investment portfolios and reduce overall risk.
-
Silver:
- Potential for Higher Returns: Silver’s industrial demand and price volatility can lead to higher returns during periods of economic growth.
- Industrial Growth: Silver’s use in various industries makes it a potential beneficiary of technological advancements and economic expansion.
- Dual Nature: Silver’s characteristics as both a precious metal and an industrial commodity offer diversification opportunities.
Risks of Gold and Silver Investment:
While gold and silver offer potential benefits, investors must be aware of associated risks:
- Price Volatility: Both metals can experience significant price fluctuations, particularly in the short term.
- Lack of Income: Gold and silver do not generate dividends or interest payments, making them passive investments.
- Storage Costs: Storing physical gold and silver requires secure facilities and incurs storage costs.
- Counterparty Risk: Investing in gold and silver through exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or other financial instruments exposes investors to counterparty risk.
FAQs on Gold vs. Silver Comparison:
1. Which is a better investment, gold or silver?
There is no definitive answer to this question, as the best investment depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and market outlook. Gold offers more stability and serves as a safe haven asset, while silver potentially offers higher returns but comes with greater risk.
2. Is gold a better inflation hedge than silver?
Historically, gold has been considered a more reliable inflation hedge than silver. However, silver’s industrial demand can also act as a hedge against inflation, particularly during periods of economic growth.
3. Is silver a good investment for long-term growth?
Silver’s long-term growth potential is tied to its industrial demand and technological advancements. While it has historically demonstrated higher price volatility than gold, it can offer higher returns during periods of economic expansion.
4. How do I invest in gold and silver?
There are various ways to invest in gold and silver, including:
- Physical Gold and Silver: Purchasing physical gold and silver bars or coins allows for direct ownership.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs tracking gold and silver prices provide a convenient and liquid way to invest.
- Mining Stocks: Investing in mining companies that extract gold and silver can provide exposure to the metals’ prices.
- Gold and Silver Futures Contracts: Futures contracts allow investors to speculate on the future price of gold and silver.
Tips for Investing in Gold and Silver:
- Define Investment Goals: Clearly define your investment objectives and risk tolerance before investing in precious metals.
- Diversify Portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your investments across different asset classes to mitigate risk.
- Conduct Thorough Research: Understand the factors that influence gold and silver prices and the risks associated with investing in them.
- Consider Storage Costs: If investing in physical gold or silver, factor in the costs of secure storage.
- Monitor Market Trends: Stay informed about market conditions and economic developments that can impact precious metal prices.
Conclusion:
Gold and silver, two enduring precious metals, continue to hold significance in the modern world. Their historical importance, economic implications, and investment potential make them compelling assets for individuals and institutions alike. While both metals share certain characteristics, their distinct attributes, market dynamics, and investment risks necessitate careful consideration. By understanding the nuances of gold and silver comparison, investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and risk appetite. Ultimately, the choice between gold and silver depends on individual circumstances and investment objectives.


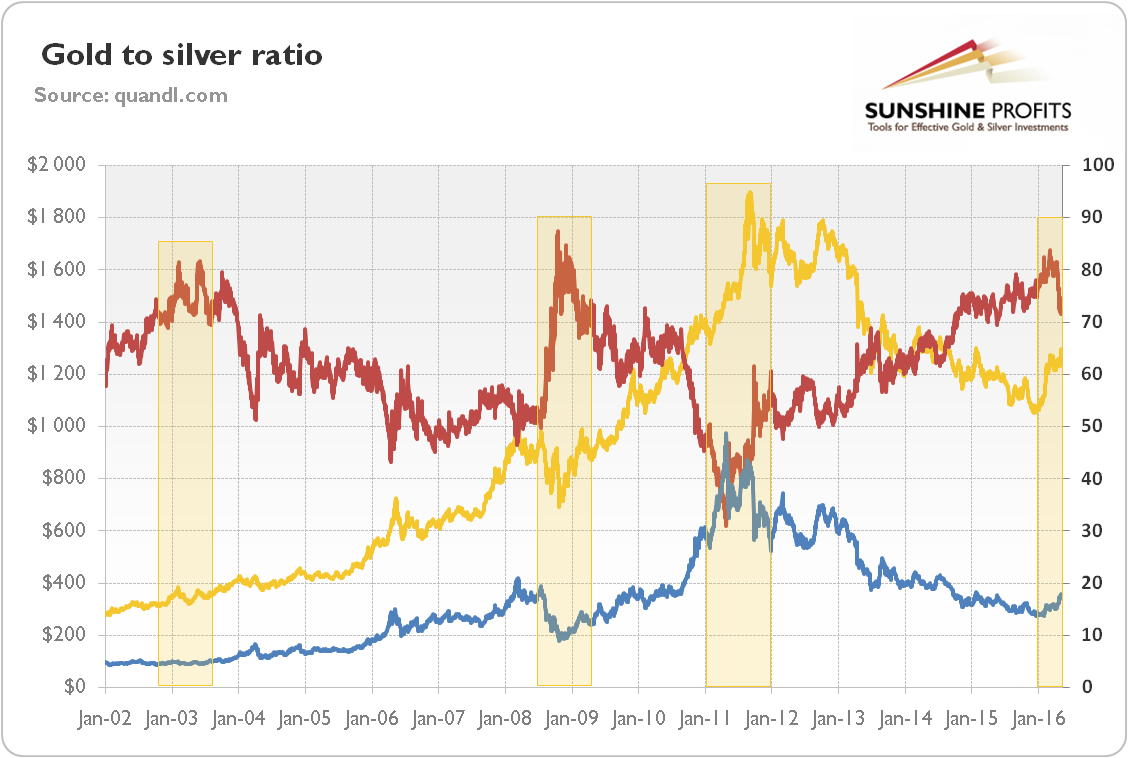
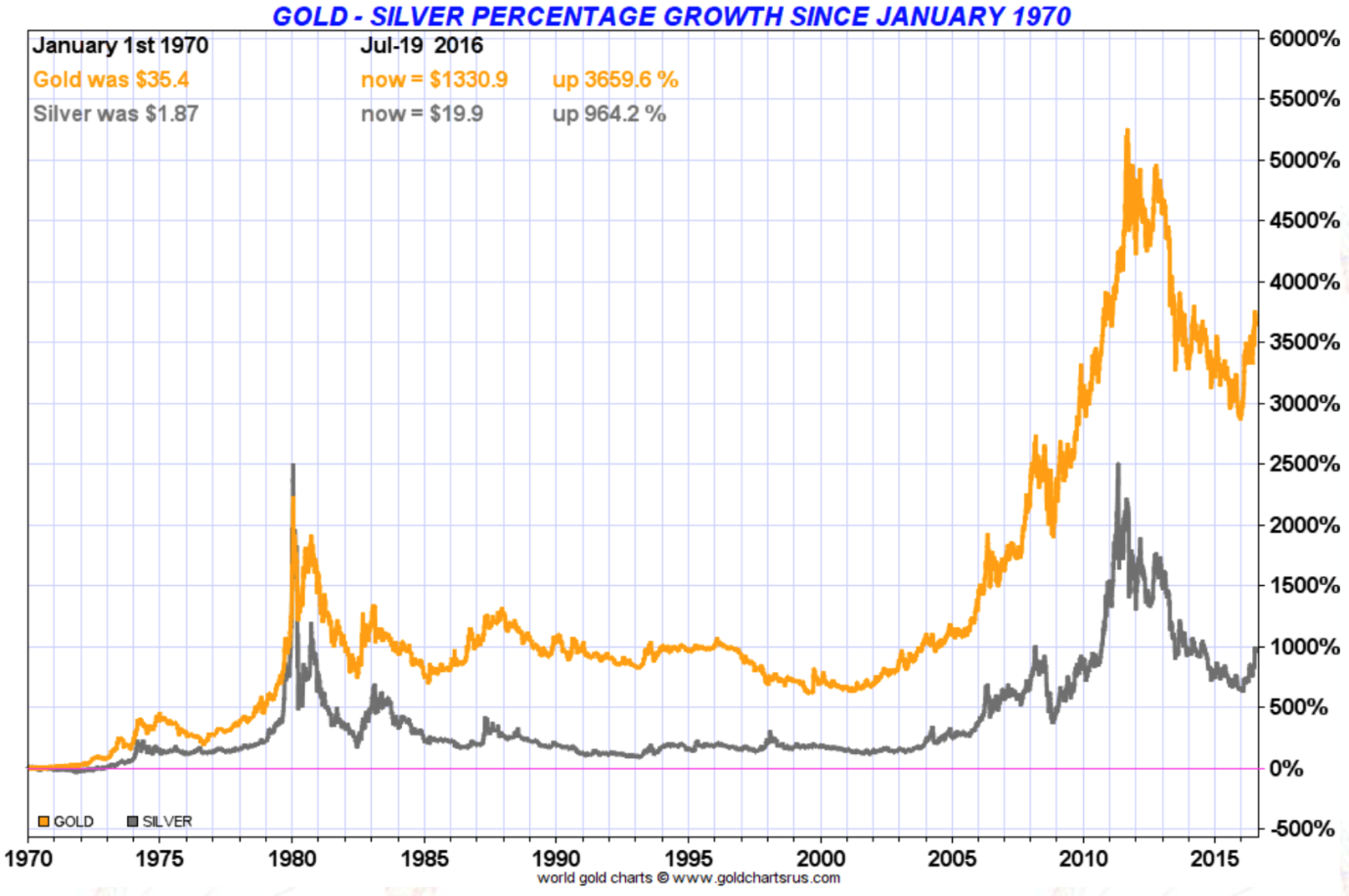


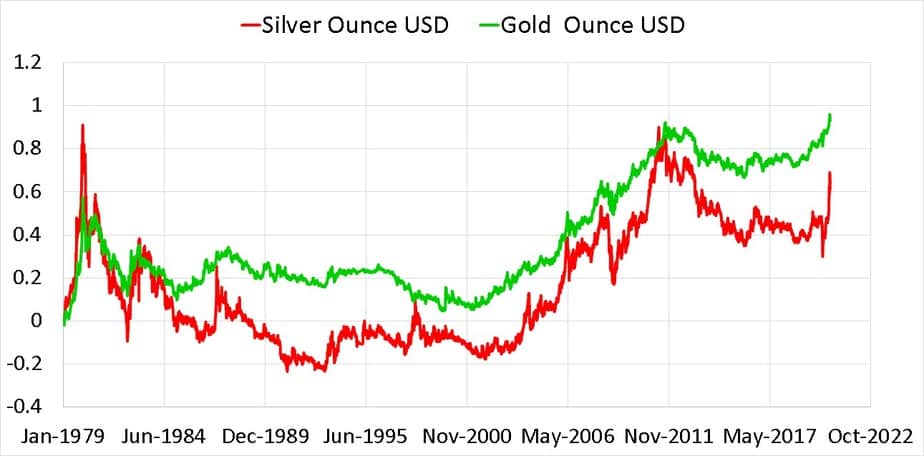
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into gold and silver comparison. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!